In this lab I will provide high level overview of DPoE system. DPoE stands for DOCSIS Provisioning over EPON. It is a migration from legacy CMTS/CM HFC (Hybrid Fiber Coax) based system to OLT/ONU EPON fiber based system.
Terminology
DOCSIS:Data Over Cable System Interface Specification EPON:Ethernet Passive Optical Network DPoE:DOCSIS Provisioning over EPON OLT:Optical Line Termination ONU:Optical Network Unit vCM:virtual Cable Modem.vCM resides in DML, it is a software entity CM:Cable Modem.It is DOCSIS terminology but still used in DPoE. DML:DOCSIS Mediation Layer
What is DOCSIS
DOCSIS stands for Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification. Cable companies are providing data over coax hybrid fiber coax (HFC) for long time. DOCSIS standard was introduced in late 90’s. The main issue with DOCSIS is the upstream/downstream rate, it is limited to less than 100 mbps. Which is slow from today’s standard. In DOCSIS 3.0 multiple channels can be bonded together to achieve gigabit rate but with continuous increase in bandwidth demand gigabit is not sufficient that’s where EPON comes into picture. EPON can provide up to 10 gigabit upstream/downstream rate. It is fiber based transport technology.
What is DPoE
DPoE stands for DOCSIS Provisioning over EPON. EPON stands for Ethernet Passive Optical Network. DPoE is a merger of two technologies, DOCSIS and EPON, to be specific it is merger of DOCSIS OSS and EPON transport.
While cable companies are upgrading last mile network to EPON based, they wanted to manage it with same OSS infrastructure they have been using for DOCSIS and why not it is a proven OSS, if it is not broken why replace it. The D in DPoE means DOCSIS OSS. DOCSIS OSS comprised of TFTP server, DHCP server, SNMP manager etc. But in order to support DOCSIS OSS in DPoE some changes are required i.e DPoE CPE device (ONU-Optical Network Unit) is not IP cable while DOCSIS CM it is IP cable. DOCSIS OSS can directly communicate with CM for service configuration. In DPoE CPE devices are virtualized.
The virtualization of CPE devices are achieved by introducing a new layer of software it is called DOCSIS Mediation Layer (DML). The purpose of DML is to virtualize CM and make it IP reachable so existing OSS can be seamlessly integrated. DML uses eOAM (extended OAM) messages to communicate with ONU (or CM). Below picture explain difference between DOCSIS and DPoE from management point of view. In DPoE OSS talks to vCM instead of physical device at customer premises.
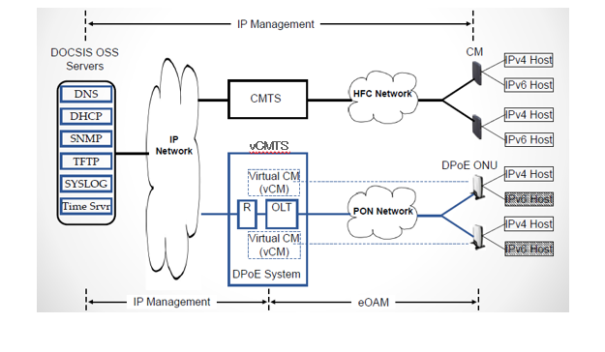
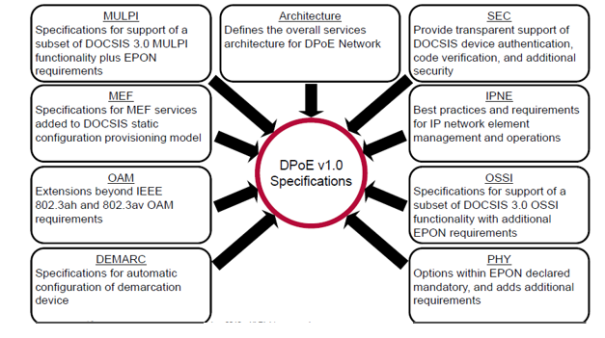
DPoE standard specifications are developed by Cable Labs. You can find documents here. DPoE requirements are divided into seven documents.
DOCSIS Configuration file
DOCSIS OSS uses configuration file to configure ONU. Configuration files are arranged in TLV (Type Length Value) format. DPoE system inherits many DOCSIS TLVs and also adds specific TLVs for DPoE. Configuration file typically contains upstream, downstream flow parameters, QOS and Vlan encapsulation TLVs
ONU turn-up process
Below two pictures explains vCMs creation in DML and how configuration file get pushed into ONU to turn up a service in DPoE system

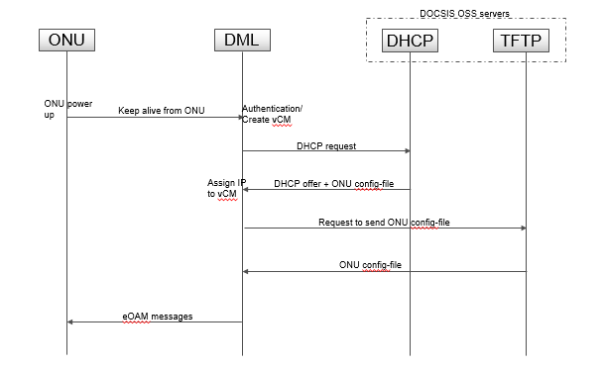
Step-0:DML discovers ONU, performs authentication and creates a vCM for ONU. vCM to ONU is 1:1 relation
Step-1:DML sends DHCP discover to DHCP server on behalf of vCM. DML uses DHCP relay function so DHCP server is pre-provisioned in the OLT.
Step-2:DHCP server sends IP address and configuration file name for the ONU. DML assigns IP to vCM.
Step-3:DML sends request to TFTP server to fetch configuration file.
Step-4:TFTP server sends configuration file to DML
Step-5:DML parses the configuration file perform syntax check, if syntax fail file rejected. It converts configuration file TLVs to eOAM messages and send it to ONU. ONU provision the service
As you can see it is a zero touch provisioning as far ONU is concerned. For test environment you can use Linux DHCP and TFTP packages
DOCSIS Configuration file format
- Configuration file is made of multiple TLVs (Type Length Value), TLV further divided into sub-TLVs.
- All TLVs are well defined in DPoE specs
- Configuration files are located in TFTP server
- DHCP server contains name of configuration file for an ONU
You will need a special editor to create or modify configuration file. Editor generates binary file when configuration is saved.
Below is an example of configuration file

Common configuration file TLVs:
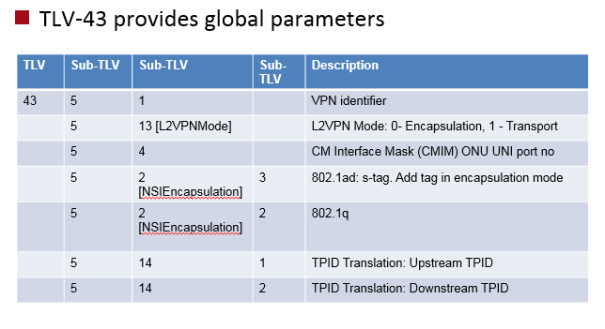
- TLV-43 – DOCSIS Extension Field
- TLV-22 – Upstream classifier
- TLV-23 – Downstream classifier
- TLV-24 – Upstream Service Flow
- TLV-25 – Downstream Service Flow
TLV-43 contains VLAN encapsulation, VLAN TPID translation and the ONU mode of operation
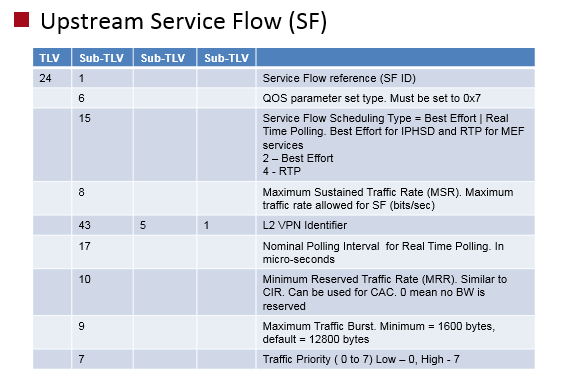
Upstream service flow contains QOS information for a flow in upstream direction
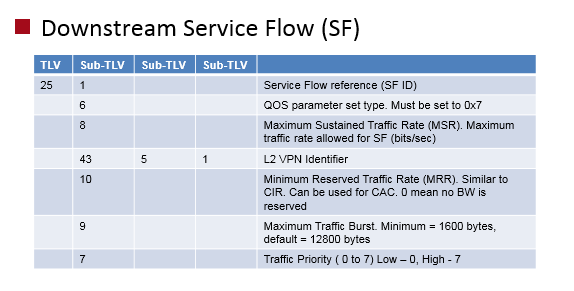
Downstream service flow contains QOS information for a flow in downstream direction
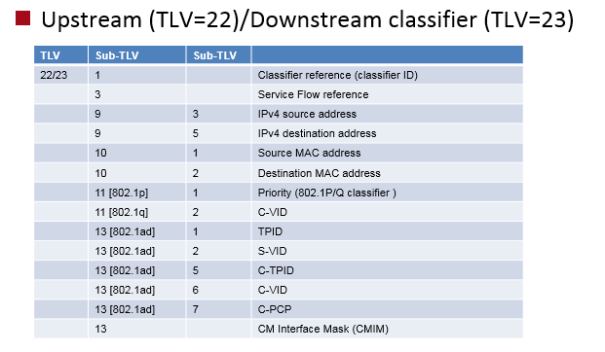
Upstream and downstream classifier contains classifier type, traffic classification can be based on MAC, IP or VLAN ID
DPoE services
DPoE provides two types of services
MEF L2 services:Mainly targeted for business. L2 services provides VLAN based switching. DPoE v1.0 calls for EPL type of service. In the upstream direction from CPE to ONU, ONU adds VLAN tag, in the downstream direction from ONU to CPE ONU strips VLAN tag. Single tagged, double tagged and TPID translation functions are supported. Switching on OLT is VLAN based
L3 services:L3 services in DPoE is called IPHSD (IP High Speed Data). It is targeted for residential. OLT supports routing protocols (OSPF, BGP), in the upstream direction forwarding is based on routing in the downstream direction forwarding is MAC based. In case of